The Pelvic Floor and Puborectalis: Unraveling Their Role in Constipation
Constipation is a common gastrointestinal issue that can lead to discomfort and inconvenience. While dietary factors and hydration play a crucial role in bowel regularity, the intricate workings of the pelvic floor and the puborectalis muscle are often overlooked contributors to this condition. In this article, we'll explore the significance of the pelvic floor and the puborectalis muscle in constipation and how understanding their roles can aid in managing this concern.
The Pelvic Floor: A Complex Support System
The pelvic floor is a network of muscles, ligaments, and connective tissues that forms a supportive hammock-like structure at the base of the pelvis. It plays a pivotal role in maintaining urinary and bowel continence, sexual function, and providing stability to the pelvic organs. The puborectalis muscle, which is a part of the pelvic floor, specifically influences bowel movements and contributes to fecal control.
Puborectalis Muscle: The Bowel Gatekeeper
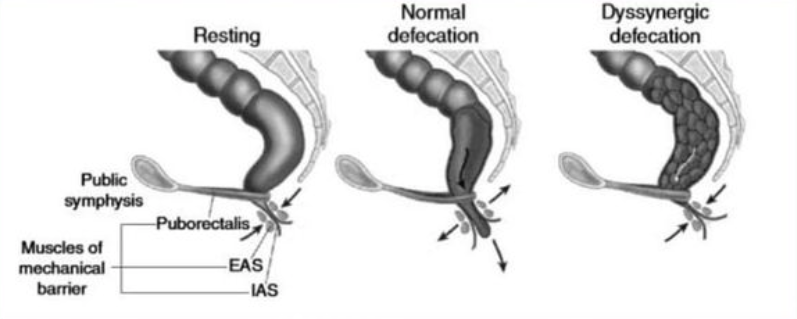
The puborectalis muscle wraps around the rectum and acts as a sphincter-like mechanism, forming a U-shaped sling that creates an angle between the rectum and the anal canal. This angle, known as the anorectal angle, helps to maintain continence by acting as a natural barrier that prevents unwanted passage of stool until it's time for a bowel movement. When it's time to defecate, the puborectalis muscle relaxes, allowing the rectum to straighten and facilitate stool passage.
Constipation and the Role of the Puborectalis Muscle
In cases of chronic constipation, the proper coordination and relaxation of the puborectalis muscle can be disrupted. Tension or excessive contraction of this muscle can lead to difficulties in straightening the rectum and allowing the passage of stool. This phenomenon, known as anismus or dyssynergic defecation, is a common cause of obstructed bowel movements. Individuals with anismus may experience straining, incomplete evacuation, and a feeling of rectal fullness.
Managing Constipation Through Pelvic Floor Awareness
Understanding the role of the puborectalis muscle in constipation can open the door to effective management strategies. Here are some approaches to consider:
1. Pelvic Floor Exercises: Engaging in targeted pelvic floor exercises, such as biofeedback and relaxation techniques, can help improve the coordination of the puborectalis muscle and enhance its relaxation during bowel movements.
2. Positioning: Maintaining the proper squatting position during defecation can aid in straightening the rectum and allowing for smoother stool passage. Consider using a footstool to elevate your feet while sitting on the toilet.
3. Diet and Hydration: Alongside pelvic floor-focused strategies, ensure you're consuming a fiber-rich diet and staying adequately hydrated. These factors contribute to healthy bowel movements.
4. Pelvic Floor Physio or colorectal surgeon: If constipation persists or worsens, consult a healthcare professional. They can provide a comprehensive evaluation, including pelvic floor assessment, and recommend appropriate treatments.
The pelvic floor and the puborectalis muscle play a significant role in maintaining proper bowel function and preventing constipation. By understanding the intricate interplay between these structures, individuals experiencing constipation can explore tailored strategies for relief and improved bowel habits. Talk to one of our pelvic floor physiotherapists today to help with managing your constipation.